Medical devices classification
Medical devices regulation
Medical devices (MD) are classified according to the rules defined in Appendix VIII of Regulation (EU) MDR 2017/745.
Definition of medical device (Article 2.1 of the MDR)
Let's start with the definition of a medical device
“Medical device” means any instrument, apparatus, equipment, software, implant, reagent, material or other article, intended by the manufacturer to be used, alone or in combination, in humans for one or more of the following specific medical purposes:
— Diagnosis, prevention, control, prediction, prognosis, treatment or mitigation of a disease
— Diagnosis, control, treatment, mitigation of injury or disability or compensation thereof
— Investigation, replacement or modification of an anatomical structure or function or of a physiological or pathological process or state
— Communication of information through in vitro examination of samples from the human body, including organ, blood and tissue donations
and whose main intended action in or on the human body is not achieved by pharmacological, immunological or metabolic means, but whose function can be assisted by such means.
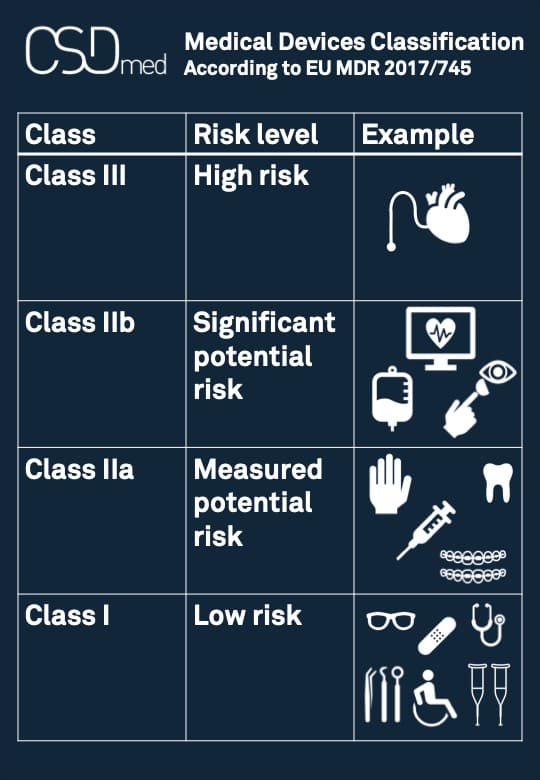
Classification of Medical Devices
The classification described in Appendix VIII is based on the level of risk:
— Class I: the lowest level of risk
— Class IIa: a moderate potential level of risk
— Class IIb: a significant potential level of risk
— Class III: the highest level of risk
Classification principles
— The classification rules are applicable to all devices: MD, accessories and devices with no medical purposes but which are listed in Annex XVI of the MDR.
— Annex VIII of the European regulation describes the classification rules: 22 rules divided into 4 groups: non-invasive, invasive, active MDs and special rules
— The manufacturer of the MD determines the classification of its device
— If several rules or, within the same rule, several “sub-rules” apply to the same device, the rule or “sub-rule” which applies is the strictest, the device being classified in the highest class (point 3.5 of Annex VIII)
Impact of classification rules on the design and monitoring of MDs
Classification of an MD will directly impact the level of requirements to be applied by the manufacturer and its notified body. This impacts, for example:
— Traceability (e.g. art. 18 for implant cards)
— Information to be communicated via EUDAMED (art. 29.4; art.32, art. 56.5)
— Conformity assessment procedures (art. 52)
— Clinical investigations (art.70)
— Post-market surveillance (PMS) (e.g. PSUR, art.86)
— etc.
Support guides for classifying MDs
— The European Commission has published guidance documents to help stakeholders implement the Medical Devices Regulation.
— These documents are legally non-binding and aim to ensure uniform application of the regulations.
For example, MDCG Guide 2021-24 on MD Classification, where MD examples are provided for each classification rule.
The list of examples has been reproduced below.
Non invasive devices
Class | Rule 1 | Examples |
I | All non-invasive devices are classified as class I, unless one of the rules set out hereinafter applies | - Devices intended in general for external patient support (e.g. hospital beds, patient hoists, walking aids, wheelchairs, stretchers, dental patient chairs) - Body liquid collection devices intended to be used in such a way that a return flow is unlikely (e.g. to collect body wastes such as urine collection bottles, incontinence pads or collectors used with wound drainage devices). They may be connected to the patient by means of catheters and tubing - Devices used to immobilise body parts and/or to apply force or compression on them (e.g. non-sterile dressings used to aid the healing of a sprain, plaster casts, cervical collars, gravity traction devices, compression hosiery) - Corrective spectacle frames (i.e. glasses) and lenses in frames - Stethoscopes - Eye occlusion plasters - Incision drapes - Non-invasive conductive gels, i.e. ultrasound gels - Non-invasive electrodes (electrodes for EEG or ECG) - Permanent magnets for removal of ocular debris - Wheelchairs pushed by hand |
Class | Rule 2 | Examples |
IIa | All non-invasive devices intended for channeling or storing blood, body liquids, cells or tissues, liquids or gases for the purpose of eventual infusion, administration or introduction into the body are classified as class IIa: - if they may be connected to a class IIa, class IIb or class III active device; or if they are intended for use for channeling or storing blood or other body liquids or for storing organs, parts of organs or body cells and tissues, | - Devices intended to be used as channels in active drug delivery systems, e.g. tubing intended for use with an infusion pump - Devices used for channelling gases, e.g. antistatic tubing for anaesthesia, anaesthesia breathing circuits - Syringes for infusion pumps - Devices intended to channel blood (e.g. in transfusion, extracorporeal circulation) - Devices intended for temporary storage and transport of organs for transplantation (i.e. containers, bags) - Devices intended for long-term storage of biological substances and tissues such as corneas, sperm, human embryos, etc. (i.e. containers, bags) - Fridges/freezers specifically intended for storing blood, tissues etc. - Tubing/blood lines for extracorporeal treatment (dialysis and apheresis therapies) |
IIb | - except for blood bags; blood bags are classified as class IIb. | - Blood bags without a substance which, if used separately, can be considered to be a medicinal product |
I | In all other cases, such devices are classified as class I | - Non-invasive devices that provide a simple channelling function, with gravity providing the force to transport the liquid, e.g. administration sets for infusion - Devices intended to be used for a temporary containment or storage function, e.g. cups and spoons specifically intended for administering medicines - Empty syringes without needles |
Class | Rule 3 | |
IIb | All non-invasive devices intended for modifying the biological or chemical composition of human tissues or cells, blood, other body liquids or other liquids intended for implantation or administration into the body are classified as class IIb, | - Devices intended to remove undesirable substances out of the blood by exchange of solutes such as hemodialysers - Devices intended to separate cells by physical means, e.g. gradient medium for sperm separation - Haemodialysis concentrates - Device removing specific blood cells (e.g. activated) by specific binding to a matrix |
IIa | unless the treatment for which the device is used consists of filtration, centrifugation or exchanges of gas, heat, in which case they are classified as class IIa | - Particulate filtration of blood in an extracorporeal circulation system. These are used to remove particles from the blood - Centrifugation of blood to prepare it for transfusion or autotransfusion excluding centrifuges for manufacturing a medicinal product - Removal of carbon dioxide from the blood and/or adding oxygen - Warming or cooling the blood in an extracorporeal circulation system. |
III | All non-invasive devices consisting of a substance or a mixture of substances intended to be used in vitro in direct contact with human cells, tissues or organs taken from the human body or used in vitro with human embryos before their implantation or administration into the body are classified as class III. | - Substances or mixture of substances for transport, perfusion, storage of organs intended for transplantation that do not achieve the principal intended action by pharmacological, immunological or metabolic means - IVF or ART products without principal pharmacological/metabolic action (substances or mixture of substances) - IVF cell media without human albumin |
Class | Rule 4 | Examples |
I | All non-invasive devices which come into contact with injured skin or mucous membrane are classified as: - class I if they are intended to be used as a mechanical barrier, for compression or for absorption of exudates; | - Wound dressings for skin or mucous, such as: absorbent pads, island dressings, cotton wool, wound strips, adhesive bandages (sticking plasters, band-aid) and gauze dressings which act as a barrier, maintain wound position or absorb exudates from the wound - Ostomy bags |
IIb | - class IIb if they are intended to be used principally for injuries to skin which have breached the dermis or mucous membrane and can only heal by secondary intent; | Are principally intended to be used with severe wounds: - Dressings intended for ulcerated wounds having breached the dermis - Dressings intended for burns having breached the dermis - Dressings for severe decubitus wounds - Dressings incorporating means of augmenting tissue and providing a temporary skin substitute |
IIa | - class IIa if they are principally intended to manage the micro-environment of injured skin or mucous membrane; and | - Hydrogel dressings for wounds or injuries that have not breached the dermis or can only heal by secondary intent - Non-medicated impregnated gauze dressings - Polymer film dressings |
IIa | - class IIa in all other cases | |
! | This rule applies also to the invasive devices that come into contact with injured mucous membrane. | - Dressings for nosebleeds (the purpose of the dressing is not to manage micro-environment) are in class I according to this rule - Dental wound dressings not containing animal-derived material |
Invasive devices
Class | Rule 5 | Examples |
I | All invasive devices with respect to body orifices, other than surgically invasive devices, which are not intended for connection to an active device or which are intended for connection to a class I active device are classified as: class I if they are intended for transient use; | - Handheld mirrors used in dentistry to aid in dental diagnosis and surgery - Dental impression materials - Stomach tubes - Impression trays - Examination gloves - Urinary catheters intended for transient use - Embryo transfer catheter and insemination catheter |
IIa | - class IIa if they are intended for short-term use, | - Short term corrective contact lenses - Tracheal tubes - Indwelling urinary catheters intended for short term use - Gases used for insufflation in the body - Nasobiliary tubes |
I | - except if they are used in the oral cavity as far as the pharynx, in an ear canal up to the ear drum or in the nasal cavity, in which case they are classified as class I; and | - Materials for dental impressions - Plastic syringe used to measure a quantity of medicinal product before oral administration to the patient - Removable or fixed dental prostheses |
IIb | - class IIb if they are intended for long-term use. | - Urethral stents - Long term corrective contact lenses - Tracheal cannulae for tracheostoma for long term use - Urinary catheters intended for long term use |
IIa | - except if they are used in the oral cavity as far as the pharynx, in an ear canal up to the ear drum or in the nasal cavity and are not liable to be absorbed by the mucous membrane, in which case they are classified as class IIa. | - Orthodontic wires - Fixed dental prostheses - Fissure sealants |
IIa | All invasive devices with respect to body orifices, other than surgically invasive devices, intended for connection to a class IIa, class IIb or class III active device, are classified as class IIa | - Tracheostomy or tracheal tubes connected to a ventilator - Blood oxygen analysers placed under the eyelid - Powered nasal irrigators - Fibre optics in endoscopes connected to surgical lasers - Suction catheters or tubes for stomach drainage - Dental aspirator tips - Endoscopes using a light source in the visible spectrum |
Class | Rule 6 | Examples |
IIa | All surgically invasive devices intended for transient use are classified as class IIa unless they: | - Needles used for suturing - Needles or syringes - Lancets - Single use scalpels and single use scalpel blades - Surgical swabs - Surgical gloves - Swabs to sample exudates - Guidewires or catheters used outside the central circulatory system |
III | - are intended specifically to control, diagnose, monitor or correct a defect of the heart or of the central circulatory system through direct contact with those parts of the body, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Cardiovascular catheters (e.g. angioplasty balloon catheters, stent delivery catheters/systems), including related guidewires, related introducers and dedicated disposable cardiovascular surgical instruments e.g. electrophysiological catheters, electrodes for electrophysiological diagnosis and ablation, - Catheters containing or incorporating sealed radioisotopes, where the radioactive isotope is not intended to be released into the body, if used in the central circulatory system - Distal protection devices |
I | - are reusable surgical instruments, in which case they are classified as class I; | - Scalpels and scalpel handles - Reamers - Drill bits - Saws, that are not intended for connection to an active device - Retractors, forceps, excavators and chisels - Sternum retractors for transient use - Staplers (outside the heart, central circulatory or central nervous system) - Dental Osteotomes |
III | - are intended specifically for use in direct contact with the heart or central circulatory system or the central nervous system, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Neuro-endoscopes - Brain spatulas - Direct stimulation cannulae - Spinal cord retractors - Spinal needles - Cranium guide for use in craniotomy - Dura mater protection; Bone punch for use on the cranium (Intended use: The dura mater protection is intended to protect the dura mater during surgical procedures. It has direct contact to the CNS. The bone punch can be used at the cranium. A direct contact to the CNS is possible during application.) - Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line - Heart valve occluders, sizers and holders - Cardiovascular drainage cannula specifically intended to circulate blood whilst located in the heart or central vascular system - Cryo-ablation of the heart or spine - Appliers/Forceps for aneurysm clips |
IIb | - are intended to supply energy in the form of ionising radiation in which case they are classified as class IIb; - or | - Catheters containing or incorporating sealed radioisotopes, where the radioactive isotope as such is not intended to be released into the body, excluding the central circulatory system |
IIb | - have a biological effect or are wholly or mainly absorbed in which case they are classified as class IIb; | - Viscoelastic solution for ophthalmic surgery |
IIb | - are intended to administer medicinal products by means of a delivery system, if such administration of a medicinal product is done in a manner that is potentially hazardous taking account of the mode of application, in which case they are classified as class IIb. | - Refillable insulin pens - Analgesia pumps |
Class | Rule 7 | Examples |
IIa | All surgically invasive devices intended for short-term use are classified as class IIa unless they: | - Clamps - Infusion cannulae - Skin closure devices - Temporary filling materials - Arthroscopy trocars - Insufflation gases for surgically invasive endoscopic procedures |
III | are intended specifically to control, diagnose, monitor or correct a defect of the heart or of the central circulatory system through direct contact with those parts of the body, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Cardiovascular catheters - Cardiac output probes - Temporary pacemaker leads - Thoracic catheters intended to drain the heart, including the pericardium - Carotid artery shunts - Ablation catheter - Heart bypass cannula (aortic perfusion cannula and venous drainage cannula) - Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line and central line |
III | are intended specifically for use in direct contact with the heart or central circulatory system or the central nervous system, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Neurological catheters - Cortical electrodes - Central venous/vascular catheters |
IIb | are intended to supply energy in the form of ionizing radiation in which case they are classified as class IIb; | - Brachytherapy devices |
III | have a biological effect or are wholly or mainly absorbed in which case they are classified as class III; | - Absorbable sutures |
IIb | are intended to undergo chemical change in the body in which case they are classified as class IIb, except if the devices are placed in the teeth; or. | - Vascular closure devices - Haemostatic foams |
IIb | are intended to administer medicines, in which case they are classified as class IIb. | - Temporary dialysis catheter, CVVH catheter |
Class | Rule 8 | Examples |
IIb | All implantable devices and long-term surgically invasive devices are classified as class IIb unless they: | - Artificial ligaments for reinforcement. Dental implants and abutments - Shunts - Peripheral stents and peripheral valves - Plates - Intra-ocular lenses - Internal closure devices (including vascular closure devices) - Tissue augmentation implants (excluding breasts) - Peripheral vascular catheters for long-term use - Peripheral vascular grafts and stents - Penile implants - Non-absorbable sutures, non-biodegradable bone cements and maxillo-facial implants, visco-elastic surgical devices intended specifically for ophthalmic anterior segment surgery - Pedicle screws |
IIa | - are intended to be placed in the teeth, in which case they are classified as class IIa; | - Bridges and crowns - Dental filling materials and pins - Dental alloys, ceramics and polymers |
III | - are intended to be used in direct contact with the heart, the central circulatory system or the central nervous system, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Prosthetic heart valves - Aneurysm clips - Vascular prosthesis and stents - Central vascular catheters for long-term use - Spinal stents - CNS electrodes - Cardiovascular sutures - Permanent and retrievable vena cava filters - Septal occlusion devices - Intra-aortic balloon pumps - External left ventricular assisting devices |
III | - have a biological effect or are wholly or mainly absorbed, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Long-term absorbable sutures - Adhesives and implantable devices claimed to be bioactive through the attachment of surface coatings such as phosphoryl choline - Biodegradable Bone Cements - Elastoviscous fluids for joint movement(eg. hyaluronan of non-animal origin) |
III | - are intended to undergo chemical change in the body in which case they are classified as class III, except if the devices are placed in the teeth | |
III | - are intended to administer medicinal products, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Rechargeable non-active drug delivery systems - Peritoneal dialysis |
III | - are active implantable devices or their accessories, in which case they are classified as class III; | - Cochlear implants and accessories - Implantable cardiac pacemakers - Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD) - Leads, electrodes, adaptors for pacemakers and implantable defibrillators - Implantable nerve stimulators - Implantable bladder stimulators - Implantable sphincter stimulators - Accessories to active implantable devices (with or without contact with the heart), be it implantable or non-implantable, and active or not: - torque wrench for implantable pulse generator / implantable cardioverter defibrillator - cables for programmer / pacing system analyser - magnet for Implantable Pulse Generator / Implantable Cardioverter Generator - programmer or an external transmitter intended for activating or controlling the implantable part of the device - implantable pacemaker leads |
III | - are breast implants or surgical meshes, in which cases they are classified as class III; | - Breast implants - Breast tissue expanders - Surgical meshes for hernia repair - Tension-free vaginal tape |
III | - are total or partial joint replacements, in which case they are classified as class III, with the exception of ancillary components such as screws, wedges, plates and instruments; or | - Hip, knee - Shoulder - Ankle |
III | - are spinal disc replacement implants or are implantable devices that come into contact with the spinal column, in which case they are classified as class III with the exception of components such as screws, wedges, plates and instruments | - Spinal disc replacement implants - Spinal implants: hooks that fix the rod on the spinal column - Stems that are implantable in contact with the spinal column - Device placed in the disc space - Interbody fusion devices |
Active devices
Class | Rule 9 | Examples |
IIa | All active therapeutic devices intended to administer or exchange energy are classified as class IIa | - Electrical and/or magnetic and electromagnetic energy: - muscle stimulators - external bone growth stimulators - TENS devices - eye electromagnets - electrical acupuncture - Thermal energy: - heat exchangers, except the types described below - Mechanical energy: - powered dermatomes - powered drills - dental hand pieces - Light: - phototherapy for skin treatment and for neonatal care - Sound: - external hearing aids - Ultrasound: - equipment for physiotherapy - Sleep apnoea ventilators without monitoring function |
IIb | unless their characteristics are such that they may administer energy to or exchange energy with the human body in a potentially hazardous way, taking account of the nature, the density and site of application of the energy, in which case they are classified as class IIb. | - Kinetic energy: - lung ventilators - Thermal energy: - incubators for babies - blood warmers - electrically powered heat exchangers (with patients incapable of reacting, communicating /or who are without a sense of feeling) - Electrical energy: - high-frequency electrosurgical generators, and electrocautery equipment, including their electrodes - external pacemakers and external defibrillators with no integrated or incorporated diagnostic function - electroconvulsive therapy equipment - Coherent light: - surgical lasers - Ultrasound: - lithotripters, surgical ultrasound devices - high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) |
IIb | All active devices intended to control or monitor the performance of active therapeutic class IIb devices, or intended directly to influence the performance of such devices are classified as class IIb. | - External feedback systems for active therapeutic devices |
IIb | All active devices intended to emit ionizing radiation for therapeutic purposes, including devices which control or monitor such devices, or which directly influence their performance, are classified as class IIb | - Brachytherapy devices if the device also generates the radiation - Therapeutic cyclotrons and linear accelerators - Therapeutic X-ray sources |
III | All active devices that are intended for controlling, monitoring or directly influencing the performance of active implantable devices are classified as class III | - Programming units and pacing system analysers - Cardioscopes with pacing pulse indicators specifically intended to monitor active implantable devices - Programmer for: - implantable Pulse Generator (IPG); - implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) - implantable Loop Recorder - Remote monitoring devices for active implantable devices |
Class | Rule 10 | Examples |
IIa | Active devices intended for diagnosis and monitoring are classified as class IIa: - if they are intended to supply energy which will be absorbed by the human body, | - Magnetic resonance equipment - Pulp testers - Evoked response stimulators - Diagnostic ultrasound |
I | except for devices intended to illuminate the patient's body, in the visible spectrum, in which case they are classified as class I; | - Examination lamps - Surgical microscopes intended to illuminate the patient’s body in the visible spectrum - Dermatoscopes with integrated light sources |
IIa | - if they are intended to image in vivo distribution of radiopharmaceuticals; or | - Gamma cameras - Positron emission tomography and single-photon emission computer tomography (SPECT) |
IIa | - if they are intended to allow direct diagnosis or monitoring of vital physiological processes, | - Electrocardiographs -Electroencephalographs - Electronic thermometers - Electronic stethoscopes - Electronic blood pressure measuring equipment |
IIb | unless they are specifically intended for monitoring of vital physiological parameters and the nature of variations of those parameters is such that it could result in immediate danger to the patient, for instance variations in cardiac performance, respiration, activity of the central nervous system, or they are intended for diagnosis in clinical situations where the patient is in immediate danger, in which case they are classified as class IIb. | - Blood gas analysers used in open heart surgery - Apnoea monitors, including apnoea monitors in home care - Patient monitors (intended use: Monitor intended for multi-parameter patient monitoring. The device will produce visual and audible alarms if any of the physiological parameters monitored vary beyond pre-set limits and timed alarm recordings will be produced.), for example in intensive care monitoring, e.g. blood pressure, temperature, oxygen saturation |
IIb | Active devices intended to emit ionizing radiation and intended for diagnostic or therapeutic radiology, including interventional radiology devices and devices which control or monitor such devices, or which directly influence their performance, are classified as class IIb. | - Diagnostic X-Ray machine - Computed Tomography Devices |
Class | Rule 11 | Examples |
IIa | Software intended to provide information used to make decisions with diagnosis or therapeutic purposes is classified as class IIa, except if such decisions have an impact that may cause: | - MDSW intended to rank therapeutic suggestions for a health care professional based on patient history, imaging test results, and patient characteristics, for example, MDSW that lists and ranks all available chemotherapy options for BRCA-positive individuals. - Cognitive therapy MDSW where a specialist determines the necessary cognitive therapy based on the outcome provided by the MDSW. |
III | - death or an irreversible deterioration of a person's state of health, in which case it is in class III; or | - MDSW intended to perform diagnosis by means of image analysis for making treatment decisions in patients with acute stroke. |
IIb | - a serious deterioration of a person's state of health or a surgical intervention, in which case it is classified as class IIb. | - A mobile app intended to analyse a user’s heartbeat, detect abnormalities and inform a physician accordingly. - MDSW intended for diagnosing depression based on a score resulting from inputted data on patient symptoms (e.g. anxiety, sleep patterns, stress etc.). |
IIa | Software intended to monitor physiological processes is classified as class IIa, | - MDSW intended to monitor physiological processes that are not considered to be vital. - Devices intended to be used to obtain readings of vital physiological signals in routine check-ups including monitoring at home. |
IIb | except if it is intended for monitoring of vital physiological parameters, where the nature of variations of those parameters is such that it could result in immediate danger to the patient, in which case it is classified as class IIb. | - Medical devices including MDSW intended to be used for continuous surveillance of vital physiological processes in anaesthesia, intensive care or emergency care. |
I | All other software is classified as class I. | - MDSW app intended to support conception by calculating the user’s fertility status based on a validated statistical algorithm. The user inputs health data including basal body temperature (BBT) and menstruation days to track and predict ovulation. The fertility status of the current day is reflected by one of three indicator lights: red (fertile), green (infertile) or yellow (learning phase/cycle fluctuation). |
Class | Rule 12 | Examples |
IIa | All active devices intended to administer and/or remove medicinal products, body liquids or other substances to or from the body are classified as class IIa, | - Suction pump - Feeding pumps - Jet injectors for vaccination - Elastomeric pumps or balloon pumps for infusion |
IIb | unless this is done in a manner that is potentially hazardous, taking account of the nature of the substances involved, of the part of the body concerned and of the mode of application in which case they are classified as class IIb. | - Infusion pumps - Ventilators - Anaesthesia machines - Anaesthetic vaporisers - Dialysis equipment - Blood pumps for heart-lung machines - Hyperbaric chambers - Pressure regulators for medical gases - Medical gas mixers - Moisture exchangers in breathing circuits if used on unconscious or non-spontaneously breathing patients - Oxygen concentrator used to deliver oxygen enriched air directly to the patient |
Class | Rule 13 | Examples |
I | All other active devices are classified as class I. | - Electric wheelchairs - Dental curing lights - Electric hospital beds - Patient hoists - Dental patient chairs |
Special rules
Class | Rule 14 | Examples |
III | All devices incorporating, as an integral part, a substance which, if used separately, can be considered to be a medicinal product, as defined in point 2 of Article 1 of Directive 2001/83/EC, including a medicinal product derived from human blood or human plasma, as defined in point 10 of Article 1 of that Directive, and that has an action ancillary to that of the devices, are classified as class III. | - Bone cement with antibiotics - Condoms with spermicide - Catheters coated with anticoagulants (e. g. heparin) - Endodontic materials with antibiotics - Ophthalmic irrigation solutions principally intended for irrigation, which contain components supporting the metabolism of the endothelial cells of the cornea - Dressings incorporating an antimicrobial agent where the agent has an ancillary action on the wound - Drug eluting stents (e.g. coronary, pulmonary) - Surgical sealants containing human serum albumin or thrombin - Implants coated with human fibrinogen - Blood bags incorporating heparin or other substances as anticoagulant agents which, if used separately, can be considered to be a medicinal product - IVF cell media with human albumin - Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) containing medicinal substances including copper or silver - Catheter lubrication gels containing analgesia e.g. lidocaine |
Class | Rule 15 | Examples |
IIb | All devices used for contraception or prevention of the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases are classified as class IIb, | - Condoms and femidoms (internal condoms) - Contraceptive diaphragms - Fertility monitors and medical device software intended to be used in contraception (e.g. by using the basal body temperature) |
III | unless they are implantable or long term invasive devices, in which case they are classified as class III. | - Tubal ligation devices (e.g. clips or rings) - Non-hormonal intrauterine contraceptive devices (IUCD or ICD) |
Class | Rule 16 | Examples |
IIb | All devices intended specifically to be used for disinfecting, cleaning, rinsing or, where appropriate, hydrating contact lenses are classified as class IIb. | - Contact lens storing solutions - Cleaners for contact lenses - Ultraviolet, vibration, or ultrasonic devices for cleaning and disinfecting contact lenses |
IIa | All devices intended specifically to be used for disinfecting or sterilising medical devices are classified as class IIa, | - Disinfecting solutions specifically intended for non-invasive medical devices - Washer-disinfectors intended specifically for disinfecting non-invasive medical devices - Sterilisers intended to sterilise medical devices in a medical environment |
IIb | unless they are disinfecting solutions or washer-disinfectors intended specifically to be used for disinfecting invasive devices, as the end point of processing, in which case they are classified as class IIb. | - Solutions/disinfectors for transesophageal ultrasound probes - Washer-disinfector equipment specifically for disinfecting endoscopes or other invasive devices at the end point of processing (e. g. dental equipment) - Disinfectants for the fluid pathways of haemodialysis equipment - Denture disinfecting products |
! | This rule does not apply to devices that are intended to clean devices other than contact lenses by means of physical action only. | - Brushes specifically intended to clean medical devices by mechanical action - Ultrasonic devices (for other devices than contact lenses) |
Class | Rule 17 | Examples |
IIa | Devices specifically intended for recording of diagnostic images generated by X-ray radiation are classified as class IIa. | - Digital x-ray detectors for recording images - Photostimulable phosphor plates - X-ray films |
Class | Rule 18 | Examples |
III | All devices manufactured utilising tissues or cells of human or animal origin, or their derivatives, which are non- viable or rendered non-viable, are classified as class III, | - Animal derived biological heart valves - Porcine xenograft dressings - Devices made from animal-sourced collagen/gelatine - Devices utilising hyaluronic acid of animal origin - Substance-based devices containing collagen for use in body orifices - Collagen dermal fillers - Bone graft substitutes |
I | unless such devices are manufactured utilising tissues or cells of animal origin, or their derivatives, which are non-viable or rendered non-viable and are devices intended to come into contact with intact skin only. | - Leather components of orthopaedic appliances |
Class | Rule19 | Examples |
All devices incorporating or consisting of nanomaterials are classified as | ||
III | -class III if they present a high or medium potential for internal exposure | - Bone fillers with nanomaterials in their formulation (not polymerized before blood/tissue contact, and degradable) - Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Intended use: thermal ablation of tumors or thermal modulation of the tumor microenvironment by submission to alternating magnetic fields) - Intravascular catheter made of non-degradable polymer, with nano-coating |
IIb | - class IIb if they present a low potential for internal exposure | - Bone fixation screws/plates with a strongly bound nano-coating potential - Solution administration set made of non-degradable polymer, with a strongly bound nano-coating |
IIa | - class IIa if they present a negligible potential for internal exposure | - Intravascular catheter for short term use made of non-degradable polymer, with nanomaterial embedded in the polymer matrix - Solution administration set made of non-degradable polymer, with nanomaterial embedded in the polymer matrix - Dental filling materials |
Class | Rule 20 | Examples |
IIa | All invasive devices with respect to body orifices, other than surgically invasive devices, which are intended to administer medicinal products by inhalation are classified as class IIa, | - Spacer intended for metered dose inhalers (attached to the inhaler) unless treating life-threatening conditions. - Inhalers for nicotine replacement therapy (nicotine not included) - Oxygen delivery system with a nasal cannula unless treating life-threatening conditions - Inhalers and nebulisers in case their mode of action is unlikely to have an essential impact on the efficacy and safety of the administered medicinal product or which are not intended to treat life-threatening conditions |
IIb | unless their mode of action has an essential impact on the efficacy and safety of the administered medicinal product or they are intended to treat life-threatening conditions, in which case they are classified as class IIb | - Nebulisers (not pre-charged with a specific medicinal product) where the failure to deliver the appropriate dosage characteristics could be hazardous - Spacer intended for metered dose inhalers attached to the inhaler. |
Class | Rule 21 | Examples |
III | Devices that are composed of substances or of combinations of substances that are intended to be introduced into the human body via a body orifice or applied to the skin and that are absorbed by or locally dispersed in the human body are classified as: - class III if they, or their products of metabolism, are systemically absorbed by the human body in order to achieve the intended purpose; | |
III | - class III if they achieve their intended purpose in the stomach or lower gastrointestinal tract and they, or their products of metabolism, are systemically absorbed by the human body; | - Na/Mg alginate, xyloglucan - Fat absorbers that are systemically absorbed, themselves or their metabolites |
IIa | - class IIa if they are applied to the skin or if they are applied in the nasal or oral cavity as far as the pharynx, and achieve their intended purpose on those cavities; and | - Substance-based formulations for skin treatment - Salt water used e.g. as nose or throat sprays - Oral cough treatments achieving their intended purpose in the oral cavity as far as the pharynx |
IIb | - class IIb in all other cases. | - Simethicone preparations for oral administration - Active charcoal for oral administration - Gel for vaginal moisturizing / vaginal lubricants - Eye drops for hydration - Ear drops - Medical devices, for oral administration, for the treatment of diarrhoea, e.g. kaolin, diosmectite - Medical devices, for oral administration, for the treatment of obesity, e.g. fructooligosaccharides, glucomannan |
Class | Rule 22 | Examples |
III | Active therapeutic devices with an integrated or incorporated diagnostic function which significantly determines the patient management by the device, such as closed loop systems or automated external defibrillators, are classified as class III. | - Automated external defibrillators (AED) including their pads/electrodes - Semiautomatic external defibrillators - Automated closed loop insulin delivery system - Automated external infusion pumps with integrated sensors to adapt the infusion therapy - Devices in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) – used for e.g. motor control in severely paralyzed patients - Closed-loop systems for deep brain stimulation (DBS) treatment of various neurological conditions - Closed-loop dynamic neurochemical control of therapeutic interventions e.g. target-controlled anaesthesia / infusion systems |
We are at your service
Since the arrival of Regulation 2017/745, new requirements are required and form part of the documentation to be presented to the notified body (e.g. review of the in-depth clinical evaluation, PMS procedure, QC results from product validation, proof of staff skills, etc.).
CSDmed brings its expertise and a methodical approach to its clients, start-ups, manufacturers, importers and distributors of medical devices, thanks to a team of specialized experts and consultants, who will be able to address the MDR transition in its entirety.
🔗 Contact us and find out how we can help you.